Return to your Visual Studio Code Terminal window.
Create a project directory called ~/workspace/ndlab/nac.
mkdir -p ~/workspace/ndlab/nac
cd ~/workspace/ndlab/nac
Within the ~/workspace/ndlab/nac directory, create additional directories:
This directory structure will keep things organized for clarity and demonstrate some other ways to work with file structures in Ansible.
Remember that you can click the copy button in the upper right hand corner of each Visual
Studio Code Terminal section in this lab guide and then paste it into the actual VSCode terminal instead
of typing everything out!
Simply hover your mouse pointer above the upper right hand corner of the window below
to make the copy button appear.
mkdir group_vars
mkdir -p group_vars/nd
mkdir host_vars
mkdir -p host_vars/site1-fabric
mkdir collections
Create a requirements.txt file in the ~/workspace/ndlab/nac directory.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/requirements.txt
cat << EOF > ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/requirements.txt
ansible-core==2.18.12
ansible-lint==24.10.0
nac-validate==1.0.0
macaddress==2.0.2
netaddr==1.3.0
packaging==25.0
requests==2.32.5
jmespath==1.0.1
EOF
Install the Python dependencies required for the VXLAN as Code solution.
pip install -r requirements.txt
You will be working with Ansible Core release version 2.18.12. You can confirm by checking the version.
ansible --version
Upon a successful installation and verification of the Ansible version, your output should look as follows:
ansible [core 2.18.12]
config file = None
configured module search path = ['/home/pod30/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /home/pod30/.pyenv/versions/3.11.14/envs/ndlab/lib/python3.12/site-packages/ansible
ansible collection location = /home/pod30/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collections
executable location = /home/pod30/.pyenv/versions/ndlab/bin/ansible
python version = 3.11.14 (main, Jan 11 2026, 20:19:03) [GCC 11.4.0] (/home/pod30/.pyenv/versions/3.11.14/envs/ndlab/bin/python)
jinja version = 3.1.6
libyaml = True
Create an ansible.cfg file to disable hostkey checking and set your Python interpreter for the purposes of this lab.
Additionally, ND Ansible modules require the Ansible persistent_connection to have some values modified.
The command_timeout and connect_timeout are required to be set to 1000 seconds or greater.
If this is something you forget to do in your environment outside of this lab, not to worry, the modules will alert you
at execution time.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/ansible.cfg
cat << EOF > ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
interpreter_python = "$PYENV_VIRTUAL_ENV/bin/python"
host_key_checking = False
collections_path = ./collections/
callback_whitelist=ansible.posix.timer,ansible.posix.profile_tasks,ansible.posix.profile_roles
callbacks_enabled=ansible.posix.timer,ansible.posix.profile_tasks,ansible.posix.profile_roles
bin_ansible_callbacks = True
[persistent_connection]
command_timeout=7200
connect_timeout=7200
EOF
Create a requirements.yml file in the ~/workspace/ndlab/nac directory.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/requirements.yml
cat << EOF > ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/requirements.yml
collections:
- name: community.general
version: 10.6.0
- name: ansible.posix
version: 2.0.0
- name: ansible.utils
version: 6.0.0
- name: ansible.netcommon
version: 8.0.0
EOF
Install the Ansible Collection dependencies required for the VXLAN as Code solution.
ansible-galaxy collection install -r requirements.yml -p ./collections
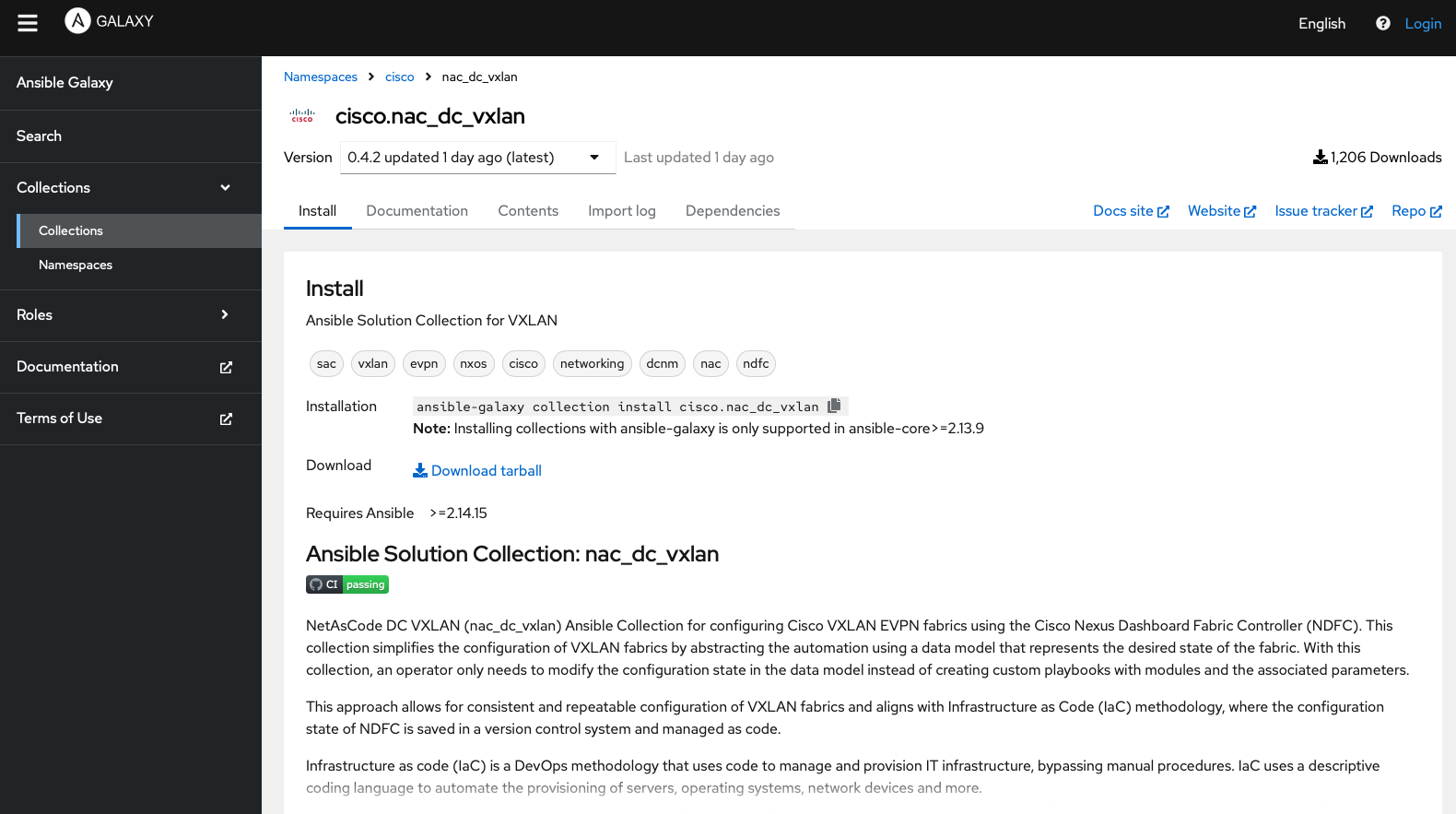
Install the nac_dc_vxlan collection which contains all the modules and plugins required to run the VXLAN as Code solution for NaC.
The ansible-galaxy collection install command is used to install this Ansible collection directly as this collection is the focal point, but you could also add it to the requirements.yml file and install it along with the other dependencies if you wanted to.
ansible-galaxy collection install cisco.nac_dc_vxlan==0.6.0 -p ./collections
Use the following ansible-galaxy command to verify the collection was installed properly and make note of the dependent collections installed; one of them should look familiar.
ansible-galaxy collection list
You should see the following output:
# /home/pod30/workspace/ndlab/ansible/collections/ansible_collections
Collection Version
----------------- -------
ansible.netcommon 8.0.0
ansible.posix 2.0.0
ansible.utils 6.0.0
cisco.dcnm 3.10.0
cisco.nac_dc_vxlan 0.6.0
community.general 10.6.0
All documentation for the VXLAN as Code (nac_dc_vxlan) Ansible collection can be found on Ansible Galaxy. Navigate to Ansible Galaxy to see the list of modules and review the documentation.

The Ansible inventory file defines how Ansible will connect and authenticate with ND. In this section you will use the lookup
plugin along with environment variables to pass sensitive information such as usernames and passwords to Ansible.
The lookup plugin allows you to access data from outside of Ansible, such as environment variables,
or files, and use that data in your playbooks. In this case, you will be using the lookup plugin to access environment variables
that you will set in a shell script. This allows you to keep sensitive information, such as passwords, out of your playbooks and inventory files,
while still being able to use them in your Ansible tasks.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/group_vars/nd/connection.yml
cat << EOF > ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/group_vars/nd/connection.yml
---
# Connection Parameters for 'nd' inventory group
#
# Controller Credentials
ansible_connection: ansible.netcommon.httpapi
ansible_network_os: cisco.dcnm.dcnm
ansible_httpapi_port: 443
ansible_httpapi_use_ssl: true
ansible_httpapi_validate_certs: false
# ansible_httpapi_login_domain: local
# ND API Credentials
ansible_user: "{{ lookup('ansible.builtin.env', 'ND_USERNAME') }}"
ansible_password: "{{ lookup('ansible.builtin.env', 'ND_PASSWORD') }}"
# Credentials for devices in Inventory
ndfc_switch_username: "{{ lookup('ansible.builtin.env', 'NDFC_SW_USERNAME') }}"
ndfc_switch_password: "{{ lookup('ansible.builtin.env', 'NDFC_SW_PASSWORD') }}"
EOF
Next, create a file named nd.yml containing parameters that control which fabric elements can be removed using the Remove role.
This acts as a safety net to prevent accidental deletions. To allow removal of specific elements, set their corresponding parameter to true in the nd.yml file.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/group_vars/nd/nd.yml
cat << EOF > ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/group_vars/nd/nd.yml
---
# Parameter to ignore diff-run
force_run_all: false
# Parameters for the tasks in the 'Remove' role
interface_delete_mode: false
inventory_delete_mode: false
link_vpc_delete_mode: false
multisite_child_fabric_delete_mode: false
multisite_network_delete_mode: false
multisite_vrf_delete_mode: false
network_delete_mode: false
policy_delete_mode: false
vpc_delete_mode: false
vrf_delete_mode: false
EOF
Now let's create a quick shell script to set environment variables for your ND username and password and ND switch username and password.
This will allow you to use the lookup plugin in your Ansible playbooks to access these environment variables.
touch ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/secrets.sh
cat <<EOF >> ~/workspace/ndlab/nac/secrets.sh
export ND_USERNAME="admin"
export ND_PASSWORD="cisco.123"
export NDFC_SW_USERNAME="admin"
export NDFC_SW_PASSWORD="cisco.123"
EOF
Source the simple shell script to set the secret env variables.
source secrets.sh
You can check if your envenv | grep -E "^ND" variables are set by issuing the below command in your VSCode terminal window:
env | grep -E "^ND"
$ env | grep -E "^ND" ND_PASSWORD=cisco.123 NDFC_SW_USERNAME=admin ND_USERNAME=admin NDFC_SW_PASSWORD=cisco.123
Navigate to the next section to begin working with VXLAN as Code.